Seed Production
Download in pdfThere are several methods for propagating plants which require both care and rigour.
- Sexual reproduction
Seed production is always to be preferred over other methods because it enables plants to be adapted to local conditions.
Seeds supplied by the Houses of Artemisia network always show some variability. The genetic and phenotypic diversity of these seeds gives a great heterogeneity of plants in the field: depending on their genes and the environment, some plants will be more suitable than others. Only seeds from plants adapted to local growing conditions should be harvested in order to obtain plants that are better suited to these conditions. The aim is to allow each House of Artemisia to select one or more varieties¹ adapted to its environment and to become autonomous in seed production.
In spite of the wide diversity of seeds and growing conditions within the network, no reports of inefficacy have been reported since 2012.
Reminder : Artemisia annua and Artemisia afra are two different species of the genus Artemisia. Consequently, there are subcategories of Artemisia annua which have different characteristics due to their different genetic material.
- Asexual reproduction
Cuttings and layering only propagate clones². These methods are to be preferred when seed propagation is difficult. These two techniques mainly concern the multiplication of Artemisia afra, whose seed viability is extremely low within the network.
Layering has a better success rate but depends on the number of stems that fall or can be bent to the ground.
Plants grown from cuttings do not have a good root system and are therefore more vulnerable to wind and drought in the first year.
[1] A plant clone is an individual or a group of individuals from a single individual (“mother plant”) made by vegetative propagation, therefore not by sexual means: the processes of cuttings, layering, splitting clumps, grafting and in vitro cell multiplication produce clones.
Definition by Etienne Cuenot, Synthesis Tela Botanica network: https://www.tela-botanica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/clone.pdf
¹ Variety: sub-classification within the same species.
Reminder : Artemisia annua and Artemisia afra are two different species of the genus Artemisia. Consequently, there are subcategories of Artemisia annua which have different characteristics due to their different genetic material.
² A plant clone is an individual or a group of individuals from a single individual (“mother plant”) made by vegetative propagation, therefore not by sexual means: the processes of cuttings, layering, splitting clumps, grafting, in vitro cell multiplication produce clones.
Definition by Etienne Cuenot, Synthesis Tela Botanica network: https://www.tela-botanica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/clone.pdf

Artemisia annua and Artemisia afra seeds are very small ovoid achenes¹. The weight of 1000 seeds is about 0.1g.
Under African conditions, the rate of flower fertilisation is generally very low. This results in the production of a very small number of seeds per flower head. The seeds supplied by the Houses of Artemisia network are produced by sieving the contents of dried flower heads after flowering. They generally contain many impurities composed mainly of aborted florets (unfertilised flowers).
The number of fertile seeds per gram of these self-produced “seeds” generally varies between 100 and 300 but may be lower in some cases.
It is estimated that a good seed plant yields 25 g of these self-produced “seeds”, giving between 2,500 and 7,500 fertile seeds.
The germination rate is extremely variable depending on the origin of the seeds, storage conditions and the local environment.
La Maison de l’Artemisia provides seeds from organic farming and asks that this method of cultivation is respected.
¹ Achene : Dry one-seeded fruit that does not open to release the seed http://herbierfrance.free.fr/lexique.htm
Selection of seed plants
It is necessary to reserve seed plants for subsequent seed harvesting. Do not choose plants that flower early!
Which plants to choose:
- The finest and most productive plants to ensure maximum production of quality herbal tea per plant.
- Plants that are less vulnerable to pest and diseases.
Choice of a resistant cultivar = the most effective means of control and is always to be preferred, even if yield is slightly lower than with another non-resistant plant, because this avoids considerable production and financial losses when pests and disease reappear. - Plants located close to each other to allow for cross-fertilisation.
Artemisia annua plants are essentially self-incompatible in terms of fertilisation. Therefore, at least two adjacent seed plants are required for good seed production.
before pruning and/or harvesting (e.g. with a ribbon).
the leaves of Artemisia annua seed plants as this may limit the amount of seeds produced.
after flowering to encourage seed production.
ss soon as the fruit has set, by watering the plants at the crown and not by sprinkling, as the moisture will cause the fruit to rot.
from wind to prevent seeds flying away.
until the leaves dry and the whole plant turns brown (1 or 2 months) to allow the seeds to form properly and have time to ripen.
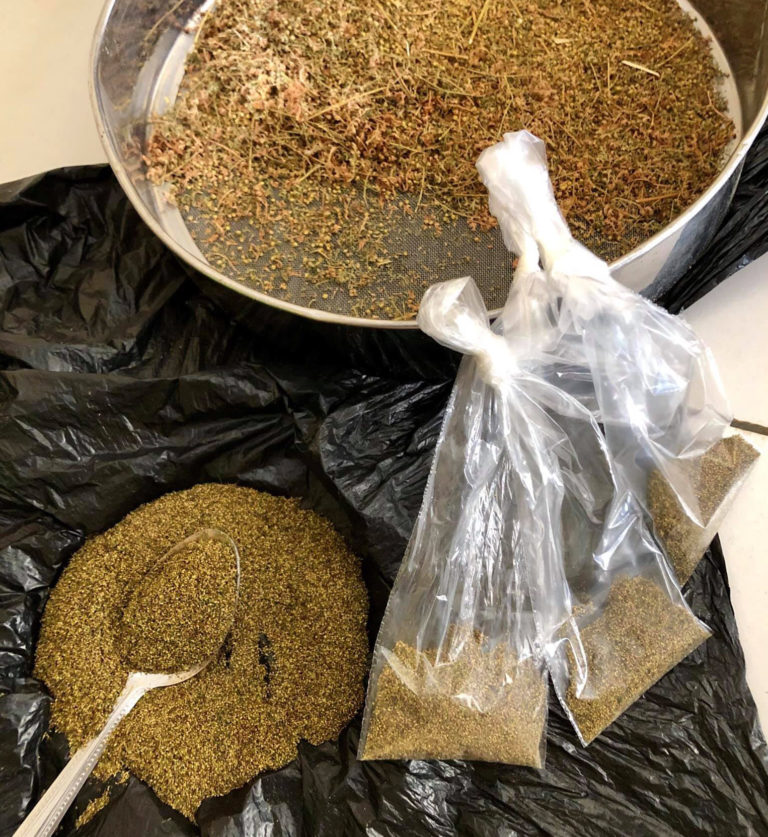
Seed collection
Do not harvest the seeds too early (they must have time mature correctly) or too late (seeds will fall to the ground and be lost).
- When the fruit takes on a grey colour, test the ripeness of the seeds on a sample: if they are well formed, they are whitish and fall when the branch is tapped.
- Cut mature Artemisia annua seed plants at the base OR remove mature seed-bearing branches of Artemisia afra.
- Dry on a clean tarpaulin or sheet and protect from moisture if the weather is humid.
- Tap the branches with a clean, dry stick to release the contents of the flower heads (seeds + flower pieces).
OR shake over a basin, tarpaulin, sheet or clean, dry plastic cover. - Sift the crop to remove as many impurities as possible.
You can use a kitchen strainer and then a coarse-mesh sieve.
Seeds can be winnowed to ensure that they are very clean. A simple sieve with a very fine mesh is all you need.
NB: this is the same process as for market garden plants of the Asteraceae family.

Never use leaves from seed plants for herbal tea as they no longer contain active molecules!
Seed storage
Store seeds away from light, moisture and heat in a tightly sealed plastic or glass bottle.
Drying systems can be used, such as silica gel, rice or charcoal.
The pot of seeds can be stored in the ground to keep seeds cool and protected from light.
Seeds can be stored for up to 3 years at room temperature, but seeds produced under African conditions generally lose their germinative power after one year.
Never put self-produced seeds in the refrigerator as this will drastically reduce germination!










